简介
如今,软件通常会作为一种服务来交付,它们被称为网络应用程序,或软件即服务(SaaS)。12-Factor 为构建如下的 SaaS 应用提供了方法论:
- 使用标准化流程自动配置,从而使新的开发者花费最少的学习成本加入这个项目。
- 和操作系统之间尽可能的划清界限,在各个系统中提供最大的可移植性。
- 适合部署在现代的云计算平台,从而在服务器和系统管理方面节省资源。
- 将开发环境和生产环境的差异降至最低,并使用持续交付实施敏捷开发。
- 可以在工具、架构和开发流程不发生明显变化的前提下实现扩展。
这套理论适用于任意语言和后端服务(数据库、消息队列、缓存等)开发的应用程序。
背景
这套方法论由Heroku的联合创始人Adam Wiggins发掘,应用到了数以百计的应用程序的开发和部署,并通过 Heroku 平台间接见证了数十万应用程序的开发,运作以及扩展的过程。
The Twelve-Factor App系列文章,综合了Hero库关于 SaaS 应用几乎所有的经验和智慧,是开发此类应用的理想实践标准,并特别关注于应用程序如何保持良性成长,开发者之间如何进行有效的代码协作,以及如何 避免软件污染 。
英文原文
VIII. Concurrency
Scale out via the process model
Any computer program, once run, is represented by one or more processes. Web apps have taken a variety of process-execution forms. For example, PHP processes run as child processes of Apache, started on demand as needed by request volume. Java processes take the opposite approach, with the JVM providing one massive uberprocess that reserves a large block of system resources (CPU and memory) on startup, with concurrency managed internally via threads. In both cases, the running process(es) are only minimally visible to the developers of the app.
Scale is expressed as running processes, workload diversity is expressed as process types.
In the twelve-factor app, processes are a first class citizen. Processes in the twelve-factor app take strong cues from the unix process model for running service daemons. Using this model, the developer can architect their app to handle diverse workloads by assigning each type of work to a process type. For example, HTTP requests may be handled by a web process, and long-running background tasks handled by a worker process.
This does not exclude individual processes from handling their own internal multiplexing, via threads inside the runtime VM, or the async/evented model found in tools such as EventMachine, Twisted, or Node.js. But an individual VM can only grow so large (vertical scale), so the application must also be able to span multiple processes running on multiple physical machines.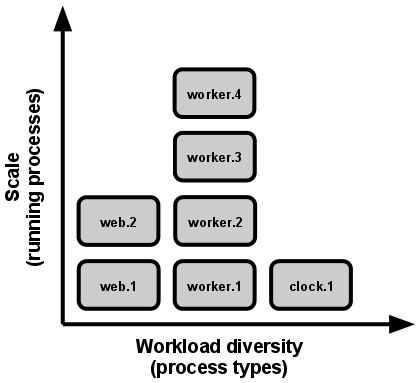
The process model truly shines when it comes time to scale out. The share-nothing, horizontally partitionable nature of twelve-factor app processes means that adding more concurrency is a simple and reliable operation. The array of process types and number of processes of each type is known as the process formation.
Twelve-factor app processes should never daemonize or write PID files. Instead, rely on the operating system’s process manager (such as systemd, a distributed process manager on a cloud platform, or a tool like Foreman in development) to manage output streams, respond to crashed processes, and handle user-initiated restarts and shutdowns.
中文
VIII. 并发
通过进程模型进行扩展
任何计算机程序,一旦启动,就会生成一个或多个进程。互联网应用采用多种进程运行方式。例如,PHP 进程作为 Apache 的子进程存在,随请求按需启动。Java 进程则采取了相反的方式,在程序启动之初 JVM 就提供了一个超级进程储备了大量的系统资源(CPU 和内存),并通过多线程实现内部的并发管理。上述 2 个例子中,进程是开发人员可以操作的最小单位。
扩展表现为运行中的进程,工作多样性表现为进程类型。
在 12-factor 应用中,进程是一等公民。12-Factor 应用的进程主要借鉴于 unix 守护进程模型 。开发人员可以运用这个模型去设计应用架构,将不同的工作分配给不同的 进程类型 。例如,HTTP 请求可以交给 web 进程来处理,而常驻的后台工作则交由 worker 进程负责。
这并不包括个别较为特殊的进程,例如通过虚拟机的线程处理并发的内部运算,或是使用诸如 EventMachine, Twisted, Node.js 的异步/事件触发模型。但一台独立的虚拟机的扩展有瓶颈(垂直扩展),所以应用程序必须可以在多台物理机器间跨进程工作。
上述进程模型会在系统急需扩展时大放异彩。 12-Factor 应用的进程所具备的无共享,水平分区的特性 意味着添加并发会变得简单而稳妥。这些进程的类型以及每个类型中进程的数量就被称作 进程构成 。
12-Factor 应用的进程 不需要守护进程 或是写入 PID 文件。相反的,应该借助操作系统的进程管理器(例如 systemd ,分布式的进程管理云平台,或是类似 Foreman 的工具),来管理 输出流 ,响应崩溃的进程,以及处理用户触发的重启和关闭超级进程的请