简介
如今,软件通常会作为一种服务来交付,它们被称为网络应用程序,或软件即服务(SaaS)。12-Factor 为构建如下的 SaaS 应用提供了方法论:
- 使用标准化流程自动配置,从而使新的开发者花费最少的学习成本加入这个项目。
- 和操作系统之间尽可能的划清界限,在各个系统中提供最大的可移植性。
- 适合部署在现代的云计算平台,从而在服务器和系统管理方面节省资源。
- 将开发环境和生产环境的差异降至最低,并使用持续交付实施敏捷开发。
- 可以在工具、架构和开发流程不发生明显变化的前提下实现扩展。
这套理论适用于任意语言和后端服务(数据库、消息队列、缓存等)开发的应用程序。
背景
这套方法论由Heroku的联合创始人Adam Wiggins发掘,应用到了数以百计的应用程序的开发和部署,并通过 Heroku 平台间接见证了数十万应用程序的开发,运作以及扩展的过程。
The Twelve-Factor App系列文章,综合了Hero库关于 SaaS 应用几乎所有的经验和智慧,是开发此类应用的理想实践标准,并特别关注于应用程序如何保持良性成长,开发者之间如何进行有效的代码协作,以及如何 避免软件污染 。
英文原文
I. Codebase
One codebase tracked in revision control, many deploys
A twelve-factor app is always tracked in a version control system, such as Git, Mercurial, or Subversion. A copy of the revision tracking database is known as a code repository, often shortened to code repo or just repo.
A codebase is any single repo (in a centralized revision control system like Subversion), or any set of repos who share a root commit (in a decentralized revision control system like Git).
One codebase maps to many deploys
There is always a one-to-one correlation between the codebase and the app:
- If there are multiple codebases, it’s not an app – it’s a distributed system. Each component in a distributed system is an app, and each can individually comply with twelve-factor.
- Multiple apps sharing the same code is a violation of twelve-factor. The solution here is to factor shared code into libraries which can be included through the dependency manager.
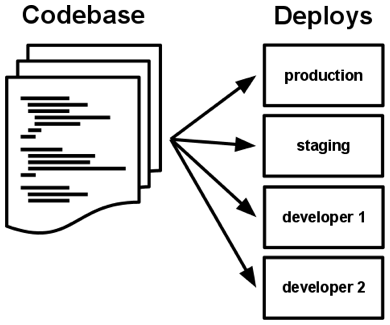
There is only one codebase per app, but there will be many deploys of the app. A deploy is a running instance of the app. This is typically a production site, and one or more staging sites. Additionally, every developer has a copy of the app running in their local development environment, each of which also qualifies as a deploy.
The codebase is the same across all deploys, although different versions may be active in each deploy. For example, a developer has some commits not yet deployed to staging; staging has some commits not yet deployed to production. But they all share the same codebase, thus making them identifiable as different deploys of the same app.
中文
I. 基准代码
一份基准代码(Codebase),多份部署(deploy)
12-Factor应用(译者注:应该是说一个使用本文概念来设计的应用,下同)通常会使用版本控制系统加以管理,如Git, Mercurial, Subversion。一份用来跟踪代码所有修订版本的数据库被称作 代码库(code repository, code repo, repo)。
在类似 SVN 这样的集中式版本控制系统中,基准代码 就是指控制系统中的这一份代码库;而在 Git 那样的分布式版本控制系统中,基准代码 则是指最上游的那份代码库。
一份代码库对应多份部署
基准代码和应用之间总是保持一一对应的关系:
- 一旦有多个基准代码,就不能称为一个应用,而是一个分布式系统。分布式系统中的每一个组件都是一个应用,每一个应用可以分别使用 12-Factor 进行开发。
- 多个应用共享一份基准代码是有悖于 12-Factor 原则的。解决方案是将共享的代码拆分为独立的类库,然后使用 依赖管理 策略去加载它们。

尽管每个应用只对应一份基准代码,但可以同时存在多份部署。每份 部署 相当于运行了一个应用的实例。通常会有一个生产环境,一个或多个预发布环境。此外,每个开发人员都会在自己本地环境运行一个应用实例,这些都相当于一份部署。
所有部署的基准代码相同,但每份部署可以使用其不同的版本。比如,开发人员可能有一些提交还没有同步至预发布环境;预发布环境也有一些提交没有同步至生产环境。但它们都共享一份基准代码,我们就认为它们只是相同应用的不同部署而已